A9655
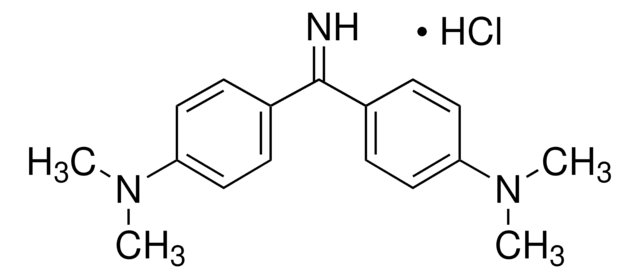
Auramine O
Dye content, ≥80%, certified by the Biological Stain Commission, powder
Synonym(s):
4,4′-(Imidocarbonyl)bis(N,N-dimethylaniline) monohydrochloride, Basic Yellow 2, Pyoctaninum aureum
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Auramine O, Dye content ≥80 %, certified by the Biological Stain Commission
grade
certified by the Biological Stain Commission
Quality Level
form
powder
composition
Dye content, ≥80%
technique(s)
microbe id | staining: suitable
color
yellow to green
mp
>250 °C (dec.) (lit.)
solubility
ethanol: 1 mg/mL, yellow to orange
λmax
370 nm in H2O
432 nm in H2O
application(s)
diagnostic assay manufacturing
hematology
histology
storage temp.
room temp
SMILES string
Cl[H].CN(C)c1ccc(cc1)C(=N)c2ccc(cc2)N(C)C
InChI
1S/C17H21N3.ClH/c1-19(2)15-9-5-13(6-10-15)17(18)14-7-11-16(12-8-14)20(3)4;/h5-12,18H,1-4H3;1H
InChI key
KSCQDDRPFHTIRL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Auramine O is used for the staining of acid-fast organisms like coccidia. Along with carbol, it generates brilliant yellow fluorochrome of tubercle bacilli. It is effective in detecting positive cases of tuberculosis. Auramine O binds to the mycolic acid in the bacterial cell wall.
Application
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Carc. 2 - Eye Irrit. 2
Storage Class
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
wgk_germany
WGK 3
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service