Recommended Products
grade
Molecular Biology
Quality Level
usage
1 kit sufficient for 150 ligation reactions
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
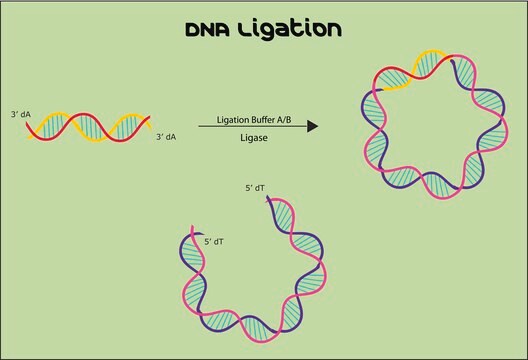
Sigma′s DNA Ligation Kit contains all of the reagents necessary to perform DNA ligation reactions. Sticky-end ligations are more efficient than blunt-end ligations; these can be facilitated with the addition of PEG.
Application
Suitable for:
- Joining fragments of DNA into a cloning vector
- Mutagenesis
- Gene anyalysis and structure-function relationships
Components
Sufficient for 150 reactions:
- 300uL 10X Ligation Buffer (D2176) in 250 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.8) 100 mM MgCl2, and 10 mM dithiothreitol
- 3 x 100 units T4 DNA Ligase (D2886) in 50% glycerol with 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) 50 mM KCl, and 1 mM dithiothreitol
- 3 x 100 uL 10 mM ATP ( A3702)
- 50 uL Control pBR322 DNA, HAE III Digest (D9430) 0.5 ug/ul in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), and 1 mM EDTA
- 1.5 mL 24% (w/v) PEG Solution, (P 2454)
- 1.5 mL Molecular Biology Grade Water (W4502)
Principle
One of the most important steps in the cloning process is the ligation of linear DNA into a cloning vector. DNA ligations are performed by incubating DNA fragments with appropriately linearized cloning vectors in the presence of buffer, ATP, and DNA ligase. Many parameters affect ligations such as the relative ratio of insert to vector, the quality and type of the DNA ends, the temperature of ligation and the concentration of DNA.
related product
Product No.
Description
Pricing
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Sambrook, J., et al
Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2, 1-1 (1989)
Quanxin Long et al.
PLoS pathogens, 13(12), e1006784-e1006784 (2017-12-30)
Hepadnavirus covalently closed circular (ccc) DNA is the bona fide viral transcription template, which plays a pivotal role in viral infection and persistence. Upon infection, the non-replicative cccDNA is converted from the incoming and de novo synthesized viral genomic relaxed
Lei Wei et al.
Nature microbiology, 5(5), 715-726 (2020-03-11)
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections result in 887,000 deaths annually. The central challenge in curing HBV is eradication of the stable covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) form of the viral genome, which is formed by the repair of lesion-bearing
Ausubel, F. M.
Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, 1, 3-3 (1994)
Bradley J Eckelmann et al.
NAR cancer, 2(3), zcaa013-zcaa013 (2020-08-11)
Homologous recombination/end joining (HR/HEJ)-deficient cancers with BRCA mutations utilize alternative DNA double-strand break repair pathways, particularly alternative non-homologous end joining or microhomology-mediated end joining (alt-EJ/MMEJ) during S and G2 cell cycle phases. Depletion of alt-EJ factors, including XRCC1, PARP1 and
Protocols
Cloning process, joining linear DNA into a vector, is crucial for biotechnological experiments, enabling DNA fragment recombinant technology.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service