PP2381
Yeast Signal Peptide Vector Set
plasmid vectors for molecular cloning
Synonym(s):
cloning vector, expression vector, molecular cloning vector, plasmid, plasmid vector, snapfast vector, vector
About This Item
Recommended Products
tag
6-His tagged
form
buffered aqueous solution
bacteria selection
kanamycin
origin of replication
2Micron
pUC (500 copies)
peptide cleavage
TEV
no cleavage
peptide tag location
N-terminal
promoter
Promoter name: TEF1
Promoter activity: constitutive
Promoter type: yeast
secretion signal
Inulase
alpha factor FL
alpha factor SP
alpha-amylase
glucoamylase
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
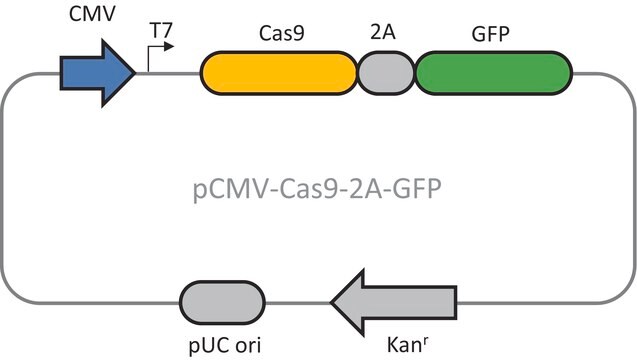
Yeast signal peptide vector set allows you to compare the activity of nine different yeast secretory tags (signal peptides) to identify which is preferred for your gene of interest. The most efficient tag seems to depend on the protein of interest and also on the cells used, hence we consider it important to compare several tags in order to select the best. Inserting your gene of interest into the MCS of these plasmids will place it downstream of the signal peptide, under regulatory control of the strong yeast TEF1 promoter.This plasmid set has been designed to be compatible with a range of cloning techniques. The multiple cloning site contains a range of standard commonly used restriction sites for cloning. Using these sites genes can be inserted using standard cloning methods with DNA ligase. Other methods such as ligase independent cloning (LIC) Gibson Assembly InFusionHD or Seamless GeneArt can also be used and because all of our plasmids are based on the same backbone the same method can be used for cloning into all of our catalogue vectors.
Multiple cloning site notes: There are a few important sites within the MCS. These include the NcoI site the XbaI site and the BsgI and BseRI sites. The NcoI site contains a start codon that is immediately downstream of both a Kozak and Shine-Dalgarno ribosomal binding site. These allow for optimal positioning of genes when the start codon is placed in this location. If this is not required and you wish to use a downstream site for gene cloning you can remove the NcoI site by cleaving the plasmid with KpnI. The XbaI site contains a stop codon. This stop codon is positioned in a specific position in relation to the BsgI and BseRI sites that are immediately downstream. When either BseRI or BsgI cleave the plasmid they produce a TA overhang from the stop codon in the XbaI site that is compatible with all of our peptide tag plasmids cut with the same sites. BseRI and BsgI sites are non-palindromic and cleave a defined number of bases away from their binding site. Whenever we clone a gene into our multiple cloning site we always position the start and stop codon in the same positions in the MCS. If the start and ends of the genes are not compatible with NcoI and XbaI we extend the sequence to the nearest external sites but keep the start and stop codons locations consistent.
Transcription Termination: Plasmids for molecular cloning contains three alternative transcription terminators for mammalian bacterial and bacteriophage (T7) expression. This means that only the promoter needs to be changed to alter the expression system you are using. We sell multiple promoters that can be used in each of these systems. The presence of each terminator does not reduce expression in the alternative systems.
Sequence
Analysis Note
Other Notes
Legal Information
Kit Components Also Available Separately
- PSF-TEF1-NH2-A-FACTOR SP - ALPHA FACTOR SECRETION PLASMID, plasmid vector for molecular cloning
- PSF-TEF1-NH2-GLUCA - GLUCOAMYLASE SECRETION PLASMID, plasmid vector for molecular cloning
- OGS1879PSF-TEF1-NH2-INTS - INVERTASE SECRETION PLASMID, plasmid vector for molecular cloningSDS
related product
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service