R9532
Pyocyanin, Ready Made Solution from Pseudomonas aeruginosa
5 mg/mL in DMSO
Synonym(s):
5-Methyl-1(5H)-phenazinone, Pyocyanine, Sanasin, Sanazin
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C13H10N2O
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
210.23
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
assay
≥98% (HPLC)
Quality Level
form
DMSO solution
concentration
5 mg/mL in DMSO
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
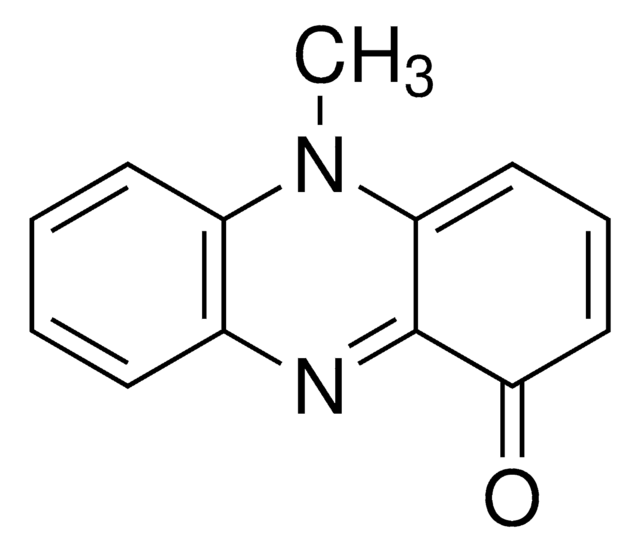
SMILES string
CN1c2ccccc2N=C3C(=O)C=CC=C13
InChI
1S/C13H10N2O/c1-15-10-6-3-2-5-9(10)14-13-11(15)7-4-8-12(13)16/h2-8H,1H3
InChI key
YNCMLFHHXWETLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Pyocyanin is a secondary metabolite, which is produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Application
Pyocyanin has been used:
- To disable the ability of forkhead box A2 (FOXA2) to regulate goblet cell hyperplasia and metaplasia (GCHM) and mucin expression.
- To activate nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (NRF2) through the reactive oxygen species (ROS)-inducible epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) cellular signal transduction pathway and its downstream effectors.
- To stimulate Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 cell line adhesion and invasion in human lung carcinoma A549 cells via reactive oxygen species (ROS) production.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Pyocyanin, a redox-active phenazine, is an electron receptor, which stimulates redox cycling in bacteria, liver cells, and human epithlial cell lines. It enhances oxidative metabolism, which increases the formation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) via reduction of NADPH. Pyocyanin also increases the release of the neutrophil chemoattractant IL-8 by airway epithelial cells both in vitro and in vivo. This involves signal transduction pathways that include oxidants, protein tyrosin kinases and MAP-kinases. IL-8 secretion by these cells is in synergy with inflammatory cytokines. Pyocyanin accelerates neutrophil apoptosis in vitro. Mice infected with a pyocyanin-deficient strain of P. aeruginosa showed elevated levels of neutrophils and neutrophil chemokines and cytokines, as well as compromised bacterial clearance from the lungs compared with mice infected with a wild type strain. This suggests that pyocyanin production by P. aeruginosa suppresses the acute inflammatory response by pathogen-driven acceleration of neutrophil apoptosis and by reducing local inflammation, and that this is advantageous for bacterial survival.
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Nuclear protein HMGN2 attenuates pyocyanin-induced oxidative stress via Nrf2 signaling and inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa internalization in A549 cells
Liu K, et al.
Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 108(8), 404-417 (2017)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyocyanin activates NRF2-ARE-mediated transcriptional response via the ROS-EGFR-PI3K-AKT/MEK-ERK MAP kinase signaling in pulmonary epithelial cells
Xu Y, et al.
PLoS ONE, 8(8), e72528-e72528 (2013)
Pyocyanin-induced mucin production is associated with redox modification of FOXA2
Hao Y, et al.
Respiratory Research, 14(1), 82-82 (2013)
Benjamin R Lundgren et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 195(9), 2087-2100 (2013-03-05)
Many pseudomonads produce redox active compounds called phenazines that function in a variety of biological processes. Phenazines are well known for their toxicity against non-phenazine-producing organisms, which allows them to serve as crucial biocontrol agents and virulence factors during infection.
Theerthankar Das et al.
PloS one, 7(10), e46718-e46718 (2012-10-12)
Bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation are both dependent on the production of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) mainly composed of polysaccharides, proteins, lipids, and extracellular DNA (eDNA). eDNA promotes biofilm establishment in a wide range of bacterial species. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service