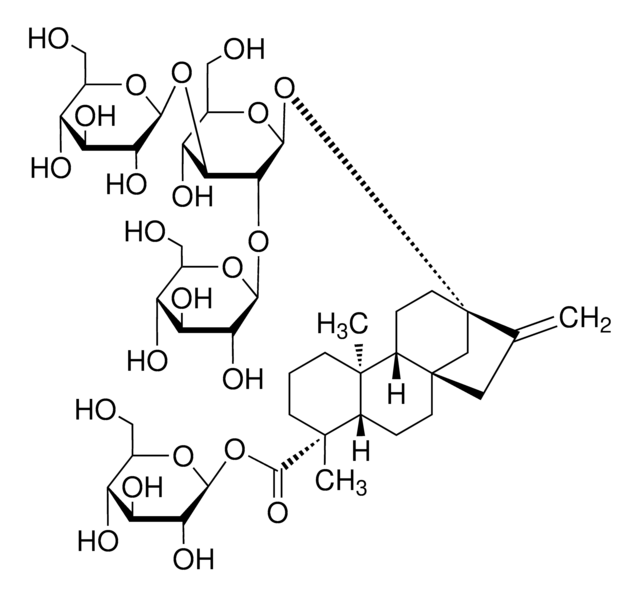
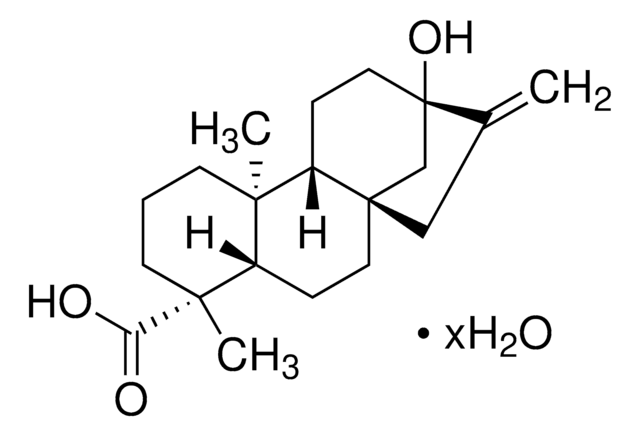
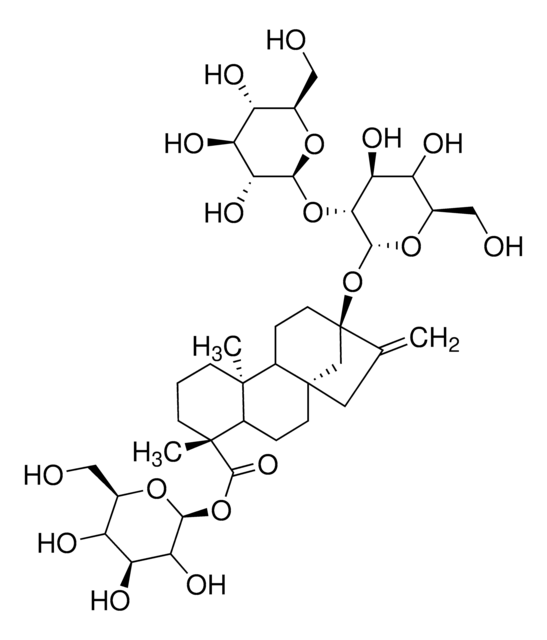
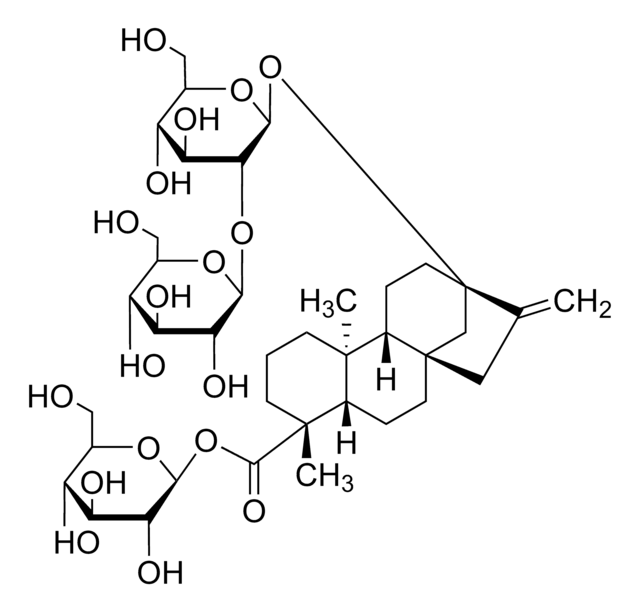
S3572
Stevioside hydrate
from Stevia sp., ≥98% (HPLC), powder, p-aminohippurate transepithelial transport inhibitor
Synonym(s):
(4α-13-[(2-O-β-D-Glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]kaur-16-en-18-oic acid β-D-glucopyranosyl ester
Select a Size
Select a Size
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Stevioside hydrate, ≥98% (HPLC)
biological source
Stevia sp.
Quality Level
assay
≥98% (HPLC)
form
powder
color
white
solubility
DMSO: 25 mg/mL, clear
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
O.C[C@@]12CCC[C@](C)(C1CC[C@]34CC(=C)[C@](CCC23)(C4)O[C@@H]5O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]5O[C@@H]6O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]6O)C(=O)O[C@@H]7O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]7O
InChI
1S/C38H60O18.H2O/c1-16-11-37-9-5-20-35(2,7-4-8-36(20,3)34(50)55-32-29(49)26(46)23(43)18(13-40)52-32)21(37)6-10-38(16,15-37)56-33-30(27(47)24(44)19(14-41)53-33)54-31-28(48)25(45)22(42)17(12-39)51-31;/h17-33,39-49H,1,4-15H2,2-3H3;1H2/t17-,18-,19-,20+,21+,22-,23-,24-,25+,26+,27+,28-,29-,30-,31+,32+,33+,35-,36-,37-,38+;/m1./s1
Related Categories
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Preparation Note
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service