おすすめの製品
アプリケーション
- 使用済みリチウムイオン電池から回収したグラファイトを導電性骨格として用いて、赤リンベースの負極に直接適用:この研究では、使用済みのリチウムイオン電池から回収したグラファイトを再利用して、赤リンベースの負極用の導電性骨格を生成し、電池用途におけるその性能と持続可能性を高めることを検討しています(Huang et al., 2023)。
- 多孔性炭素ホストへのリン酸ドープによる赤リンのリチウム貯蔵性能の向上:この研究では、多孔性炭素ホストへのリンのドーピングが赤リンのリチウム貯蔵性能を大幅に改善することが実証され、高容量のバッテリー負極のための有望なアプローチが提供されました(Han et al., 2023)。
- 高性能かつフレキシブルなリチウム硫黄電池に向けた、多硫化物の変換を加速するためのカーボンナノチューブフィルム上のレーザーアブレーション赤リン:この研究では、レーザーアブレーション技術を導入して赤リンをカーボンナノチューブフィルムに組み込み、ポリスルフィド変換と電池性能全体を向上させています(Lee et al., 2021)。
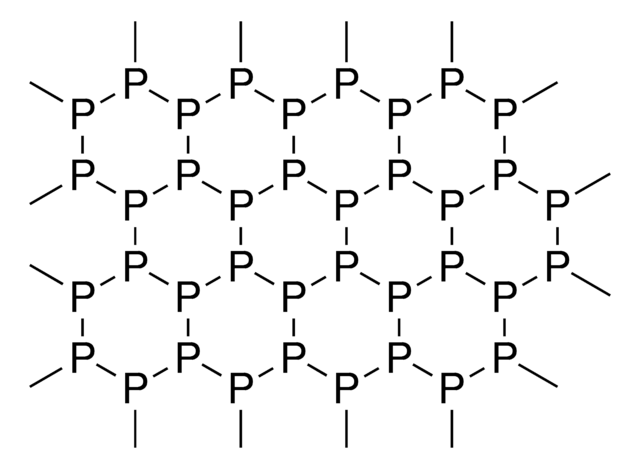
- 高性能リチウム貯蔵のための、ハニカム様多孔性ミクロンサイズ赤リンのグリーンかつテンプレート不要な合成:この論文では、電池用途におけるリチウム貯蔵能力の向上につながる、ハニカム様多孔性赤リンを生成するためのグリーンかつテンプレート不要な合成法が紹介されています(Zhu et al., 2021)。
シグナルワード
Warning
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Aquatic Chronic 3 - Flam. Sol. 2
保管分類コード
4.1B - Flammable solid hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
消防法
第2類:可燃性固体
赤りん
危険等級II
労働安全衛生法名称等を表示すべき危険物及び有害物
名称等を表示すべき危険物及び有害物
労働安全衛生法名称等を通知すべき危険物及び有害物
名称等を通知すべき危険物及び有害物
Jan Code
343242-5G:
343242-VAR:
343242-BULK:
343242-25G:
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
Manuel Delgado-Baquerizo et al.
Nature, 502(7473), 672-676 (2013-11-01)
The biogeochemical cycles of carbon (C), nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) are interlinked by primary production, respiration and decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. It has been suggested that the C, N and P cycles could become uncoupled under rapid climate change
Jacques C Finlay et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 342(6155), 247-250 (2013-10-12)
Human activities have increased the availability of reactive nitrogen in many ecosystems, leading to negative impacts on human health, biodiversity, and water quality. Freshwater ecosystems, including lakes, streams, and wetlands, are a large global sink for reactive nitrogen, but factors
Yuki Fujita et al.
Nature, 505(7481), 82-86 (2013-11-19)
Plant species diversity in Eurasian wetlands and grasslands depends not only on productivity but also on the relative availability of nutrients, particularly of nitrogen and phosphorus. Here we show that the impacts of nitrogen:phosphorus stoichiometry on plant species richness can
Bon-Chul Koo et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 342(6164), 1346-1348 (2013-12-18)
Phosphorus ((31)P), which is essential for life, is thought to be synthesized in massive stars and dispersed into interstellar space when these stars explode as supernovae (SNe). Here, we report on near-infrared spectroscopic observations of the young SN remnant Cassiopeia
René Rizzoli
The American journal of clinical nutrition, 99(5 Suppl), 1256S-1262S (2014-04-04)
Fracture risk is determined by bone mass, geometry, and microstructure, which result from peak bone mass (the amount attained at the end of pubertal growth) and from the amount of bone lost subsequently. Nutritional intakes are an important environmental factor
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)