50126
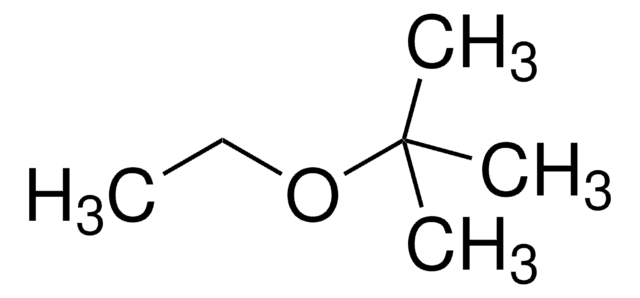
tert-ブチルメチルエーテル
suitable for HPLC, ≥99.8% (GC)
別名:
メチルtert-ブチルエーテル, メチルtert-ブチルエーテル
About This Item
おすすめの製品
蒸気密度
3.1 (vs air)
品質水準
アッセイ
≥99.8% (GC)
フォーム
liquid
自己発火温度
705 °F
シェルフライフ
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
expl. lim.
15.1 %
テクニック
HPLC: suitable
不純物
≤0.05% water
蒸発残留物質
≤0.001%
屈折率
n20/D 1.369 (lit.)
n20/D 1.369
bp
55-56 °C (lit.)
密度
0.74 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
λ
H2O reference
UV吸収
λ: 220 nm Amax: 1.0
λ: 250 nm Amax: 0.1
λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.01
アプリケーション
food and beverages
SMILES記法
COC(C)(C)C
InChI
1S/C5H12O/c1-5(2,3)6-4/h1-4H3
InChI Key
BZLVMXJERCGZMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
類似した製品をお探しですか? 訪問 製品比較ガイド
シグナルワード
Danger
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
保管分類コード
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 1
引火点(°F)
-18.4 °F - closed cup
引火点(℃)
-28 °C - closed cup
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
消防法
第4類:引火性液体
第一石油類
危険等級II
非水溶性液体
労働安全衛生法名称等を表示すべき危険物及び有害物
名称等を表示すべき危険物及び有害物
労働安全衛生法名称等を通知すべき危険物及び有害物
名称等を通知すべき危険物及び有害物
Jan Code
50126-VAR-F:
50126-25ML-F:
50126-BULK-F:
50126-4X25ML-F:
最新バージョンのいずれかを選択してください:
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)