おすすめの製品
形状
liquid
包装
vial of 50 μL
濃度
20 ng/μL in TE buffer; DNA (1μg of purified plasmid DNA)
テクニック
microbiological culture: suitable
アプリケーション
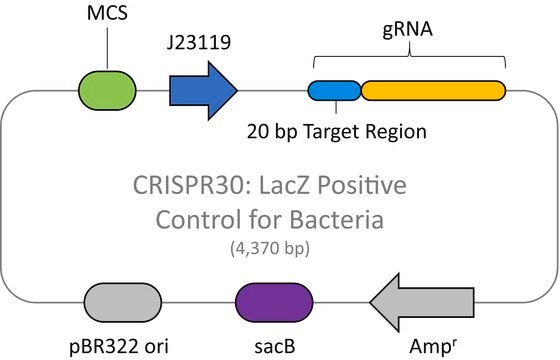
CRISPR
genome editing
プロモーター
Promoter activity: constitutive
輸送温度
dry ice
保管温度
−20°C
詳細
Here we present a novel dual-vector CRISPR/Cas-mediated λ-Red system for improved recombineering in E. coli. Our system is shown to facilitate homology-directed repair of DSBs created by Cas9 endonuclease, enabling genetic alterations through chromosomal integration of a donor DNA.
This plasmid is to be used in combination with the Cas9 Lambda Red homologous recombination plasmid for E. coli (CAS9BAC1P) as the negative control for your custom gene editing experiment. The custom gRNA (CRISPRBACD) can be designed and ordered through https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/pc/ui/genomics-home/customcrispr
The CRISPR Non-Target Negative Control Plasmid for Bacteria (CRISPR31) contains a non-targeting spacer expressed constitutively from a J23119 promoter, a ampicillin resistance marker, a pBR322 origin of replication, and a sacB gene from Bacillus subtilis for counter-selection-based curing.
アプリケーション
- HR-mediated recombineering for mutation or SNP analysis
- Creation of HR-mediated knock-in cell lines with promoters, fusion tags, or reporters integrated into endogenous genes
- Creation of gene knockouts in E. coli cell lines
Strain Optimization
特徴および利点
Markerless: does not require antibiotic resistance marker insertion
Scarless: no scar sequences from marker excision which often cause off-target recombination
Multiplexing: multiple custom gRNA sequences can be used at a time
原理
保管分類コード
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
CRISPR31-1EA:
CRISPR31-BULK:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
資料
In this article, we present an application of our novel E. coli CRISPR/Cas-mediated Lambda-Red (λ-Red) homologous recombination (HR) vector system, which facilitates gene editing through the homology-directed repair (HDR) of double-stranded DNA breaks (DSBs) created by Cas9 endonuclease, using either ssDNA or dsDNA as an editing template.
E. coli CRISPR/Cas-mediated Lambda-Red HR vector system enables gene editing via homology-directed repair.
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)