おすすめの製品
詳細
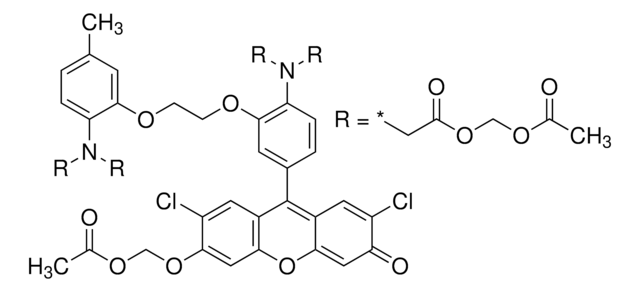
Rhodamine B labeled Ramoplanin is a fluorescent derivative of Ramoplanin, with a similar mode of action as Ramoplanin. It allows fluorescent labeling of Gram-positive bacteria and their detection by common fluorescent instruments. Ramoplanin is a lipoglycodepsipeptide antibiotic that is produced by the fermentation of Actinoplanes species. Fluorescent antibiotics are obtained by a synthetic conjugation of an antibiotic to a fluorophore.
アプリケーション
Fluorescent antibiotics can be used for many applications including:
- Antimicrobial resistance research
- Bacterial visualization and imaging
- Parent antibiotic mode of action research and new antibiotic discovery
- Toxicity studies
- Diagnosis of bacterial infections and tracking their uptake in vivo
生物化学的/生理学的作用
Ramoplanin blocks the bacterial cell wall biosynthesis by specifically binding to the first sugar of lipid I. N-Acetylmuramic acid thus interfering with peptidoglycan production.
Mode of Action: Is different from the d-Ala-d-Ala that are targeted by vancomycin and shows no cross-resistance with other glycopeptides.
Activity Spectrum: Effective against a broad-spectrum activity against Gram-positive pathogens both in vitro and in vivo including Enterococci, Staphylococci, Bacilli, Streptococci, Listeria monocytogenes, and Gram-positive anaerobes such as Clostridrium difficile. However, Rhodamine B labeled Ramoplanin presents a MIC decrease in the magnitude of two to five orders in bacterial activity in comparison to the parent Ramoplanin.
Mode of Action: Is different from the d-Ala-d-Ala that are targeted by vancomycin and shows no cross-resistance with other glycopeptides.
Activity Spectrum: Effective against a broad-spectrum activity against Gram-positive pathogens both in vitro and in vivo including Enterococci, Staphylococci, Bacilli, Streptococci, Listeria monocytogenes, and Gram-positive anaerobes such as Clostridrium difficile. However, Rhodamine B labeled Ramoplanin presents a MIC decrease in the magnitude of two to five orders in bacterial activity in comparison to the parent Ramoplanin.
特徴および利点
High quality antibiotic suitable for mulitple research applications
アナリシスノート
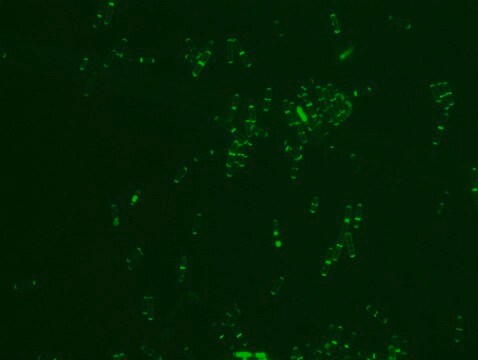
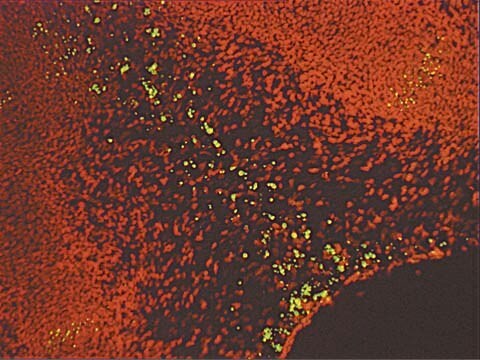
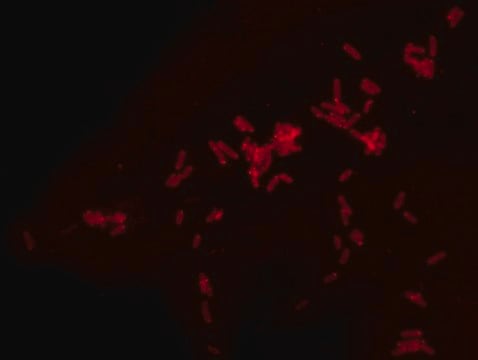
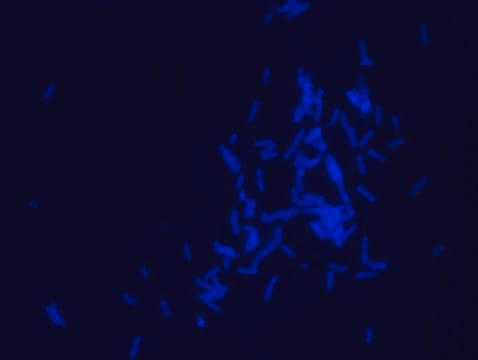
- Fluorescent microscopy application: Rhodamine B labeled Ramoplanin has excitation/emission wavelength range at 550-560 nm/590-600 nm.
- It is recommended to dissolve the Rhodamine B labeled Ramoplanin in DMSO to a concentration of 2 mg/mL.
- The recommended working concentration in fluorescent microscopy imaging application is 10μM. The mentioned concentration was used for Bacillus subtills staining (see image).
- Aliquots of the DMSO solution can be stored at −20 °C, protected from light for at least one month.
その他情報
For additional information on our range of Biochemicals, please complete this form.
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
SBR00047-BULK:
SBR00047-VAR:
SBR00047-1MG-PW:
SBR00047-1MG:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
Debra K Farver et al.
The Annals of pharmacotherapy, 39(5), 863-868 (2005-03-24)
To review the pharmacology, antimicrobial activity, pharmacokinetics, clinical applications, and safety of ramoplanin, a lipoglycodepsipeptide antibiotic. Information was obtained from MEDLINE and BIOSIS databases (1984-August 2004) and Oscient Pharmaceuticals using the key words ramoplanin, A 16686, A 16686A, and MDL
Predrag Cudic et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(11), 7384-7389 (2002-05-29)
The peptide antibiotic ramoplanin inhibits bacterial peptidoglycan (PG) biosynthesis by interrupting late-stage membrane-associated glycosyltransferase reactions catalyzed by the transglycosylase and MurG enzymes. The mechanism of ramoplanin involves sequestration of lipid-anchored PG biosynthesis intermediates, physically occluding these substrates from proper utilization
Xiao Fang et al.
Molecular bioSystems, 2(1), 69-76 (2006-08-02)
The lipoglycodepsipeptide antibiotic ramoplanin is proposed to inhibit bacterial cell wall biosynthesis by binding to intermediates along the pathway to mature peptidoglycan, which interferes with further enzymatic processing. Two sequential enzymatic steps can be blocked by ramoplanin, but there is
Kittichoat Tiyanont et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(29), 11033-11038 (2006-07-13)
The peptidoglycan (PG) layers surrounding bacterial cells play an important role in determining cell shape. The machinery controlling when and where new PG is made is not understood, but is proposed to involve interactions between bacterial actin homologs such as
M Rhia L Stone et al.
Trends in biotechnology, 36(5), 523-536 (2018-02-27)
Better understanding how multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria can evade current and novel antibiotics requires a better understanding of the chemical biology of antibiotic action. This necessitates using new tools and techniques to advance our knowledge of bacterial responses to antibiotics, ideally
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)