추천 제품
생물학적 소스
mouse
Quality Level
결합
unconjugated
항체 형태
ascites fluid
항체 생산 유형
primary antibodies
클론
GFP-20, monoclonal
분자량
antigen 27 kDa
포함
15 mM sodium azide
포장
antibody small pack of 25 μL
기술
dot blot: suitable
indirect ELISA: suitable
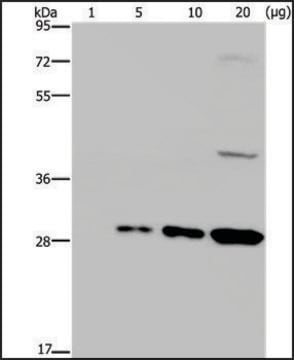
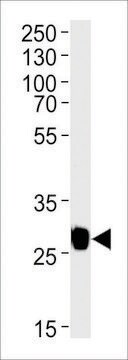
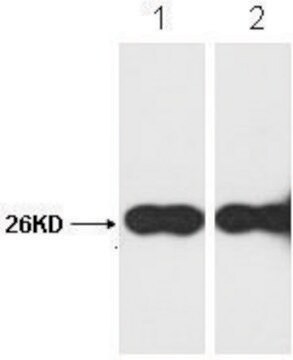
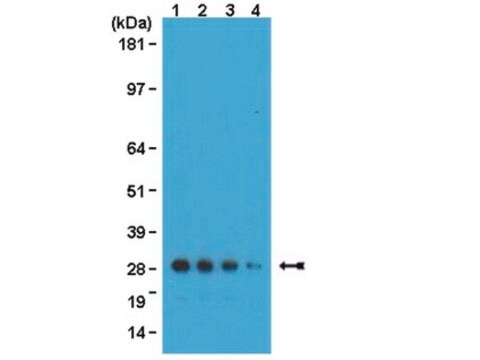
western blot: 1:2,000 using purified recombinant GFP preparation
동형
IgG1
배송 상태
dry ice
저장 온도
−20°C
타겟 번역 후 변형
unmodified
일반 설명
Monoclonal Anti-Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) (mouse IgG1 isotype) is derived from the GFP-20 hybridoma produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes from a BALB/c mouse immunized with a GFP tagged fusion protein. GFP is a 27 kDa (238 amino acid) protein, derived from the bioluminescent jellyfish Aequorea victoria, in which light is produced when energy is transferred from the Ca2+-activated photoprotein aequorin to GFP. GFP is a unique tool to monitor dynamic processes in a variety of living cells or organisms. When expressed in either eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells and illuminated by blue or UV light, GFP yields a bright green fluorescence. Light-stimulated GFP fluorescence is species-independent and a fluorescence has been reported from many different types of GFP-expressing hosts, including microbes, invertebrates, vertebrates and plants. Exogenous substrates and cofactors are not required for the fluorescence of GFP, since GFP autocatalytically forms a fluorescent pigment from natural amino acids present in the nascent protein. GFP signals can be quantified by flow cytometry, confocal scanning laser microscopy, and fluorometric assays. Indeed, many recombinant proteins have been engineered with GFP tags to facilitate the detection, isolation and purification of the proteins.
The Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) is derived from the jellyfish Aequorea Victoria and is often used as a gene expression marker. Thus, antibodies to GFP can facilitate the detection and analysis of GFP labeled nucleic acids and proteins. Monoclonal Anti-Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) antibody is specific for GFP and GFP-labeled biomolecules.
면역원
GFP tagged fusion protein
GFP tagged fusion protein.
애플리케이션
Monoclonal Anti-Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) antibody is suitable for use in western blot and ChIP assays.
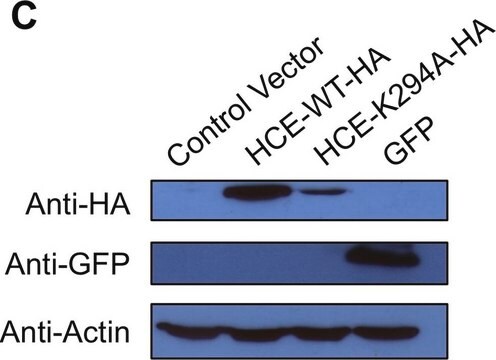
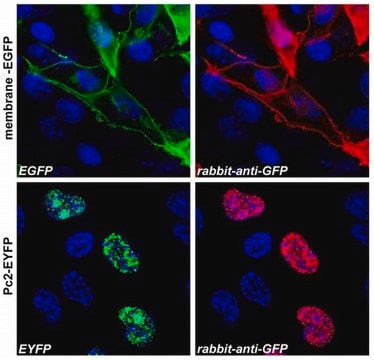
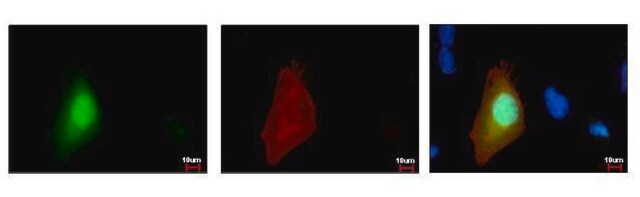
Monoclonal Anti-Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) recognizes GFP (27 kDa) using immunoblotting, dot blot, immunoprecipitation, immunocytochemistry, immunofluorescence, chromatin immunoprecipitation and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The antibody reacts with fusion proteins expressed by prokaryotes expression vectors.
면책조항
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
적합한 제품을 찾을 수 없으신가요?
당사의 제품 선택기 도구.을(를) 시도해 보세요.
관련 제품
제품 번호
설명
가격
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
이미 열람한 고객
A myosin IK-Abp1-PakB circuit acts as a switch to regulate phagocytosis efficiency
Dieckmann R, et al.
Molecular Biology of the Cell, 21(9), 1505-1518 (2010)
Gene loops juxtapose promoters and terminators in yeast
O'Sullivan JM, et al.
Nature Genetics, 36(9), 1014-1014 (2004)
Justin M O'Sullivan et al.
Nature genetics, 36(9), 1014-1018 (2004-08-18)
Mechanistic analysis of transcriptional initiation and termination by RNA polymerase II (PolII) indicates that some factors are common to both processes. Here we show that two long genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, FMP27 and SEN1, exist in a looped conformation, effectively
Enhanced stability of heterologous proteins by supramolecular self-assembly
Park JS, et al.
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 75(2), 347-355 (2007)
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor activation regulates cocaine actions and dopamine homeostasis in the lateral septum by decreasing arachidonic acid levels
Reddy IA, et al.
Translational Psychiatry, 6(5), e809-e809 (2016)
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.