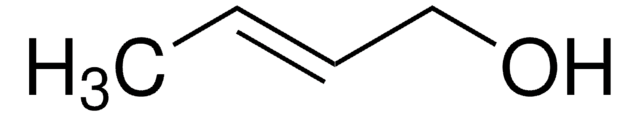
262668
Crotonaldehyde, predominantly trans
≥99%, contains 0.1-0.2% BHT as stabilizer, 1% H2O as stabilizer
Synonym(s):
(2E)-2-Butenal, (E)-But-2-en-1-al, 2(E)-Butenal, trans-2-Buten-1-al, trans-2-Butenal, trans-Crotonal
About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor density
2.41 (vs air)
vapor pressure
32 mmHg ( 20 °C)
assay
≥99%
form
liquid
autoignition temp.
320 °F
contains
0.1-0.2% BHT as stabilizer
1% H2O as stabilizer
expl. lim.
19.5 %
refractive index
n20/D 1.4362 (lit.)
bp
104 °C (lit.)
mp
−76 °C (lit.)
solubility
water: soluble 425.4 g/L at 20 °C
density
0.846 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
functional group
aldehyde
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
[H]\C(C)=C(\[H])C([H])=O
InChI
1S/C4H6O/c1-2-3-4-5/h2-4H,1H3/b3-2+
InChI key
MLUCVPSAIODCQM-NSCUHMNNSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- Crotonaldehyde (Cis and Trans): Discusses the production and properties of crotonaldehyde, including trans isomer, via aldol condensation of acetaldehyde and catalytic methods (Grant & Jenkins, 2015).
- Modeling, simulation and analysis of a process for the production of crotonaldehyde: Analyzes the production of crotonaldehyde, highlighting the stereoisomeric forms, including trans-crotonaldehyde (Scheithauer et al., 2016).
signalword
Danger
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 1 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Muta. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT RE 2 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
3 - Flammable liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
48.2 °F - closed cup
flash_point_c
9 °C - closed cup
ppe
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service