11828681001
Roche
Annexin-V-FLUOS
solution, suitable for flow cytometry
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
Recommended Products
form
solution
usage
sufficient for 250 tests
packaging
pkg of 500 μL
manufacturer/tradename
Roche
technique(s)
flow cytometry: suitable
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Annexin-V-FLUOS is a phospholipid-binding protein with a high affinity for phosphatidylserine (PS). Detection of cell-surface PS with annexin-V thus serves as a marker for apoptotic cells. Analysis may be by flow cytometry or by fluorescence microscopy.
Specificity
Annexin-V binds in a Ca2+-dependent manner to negatively charged phospholipid surfaces, and shows high affinity for phosphatidylserine.
Application
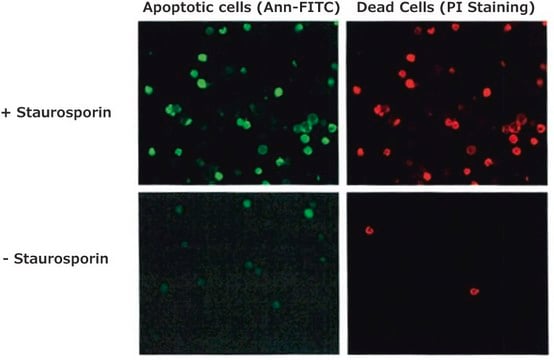
In the early stages of apoptosis, changes occur at the cell surface. One of these plasma membrane alterations is the translocation of phosphatidylserine (PS) from the inner part of the plasma membrane to the outer layer, by which PS becomes exposed at the external surface of the cell.
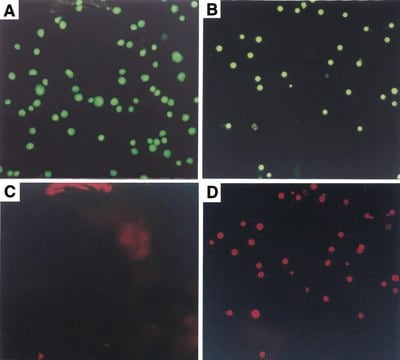
Annexin-V-FLUOS detects apoptotic cells in suspension cells using flow cytometry (FACS) or fluorescence microscopy, by binding to phosphatidylserine on the outer leaflet of apoptotic cell membranes. A simultaneous labeling with, e.g., propidium iodide (PI) is needed for differentiation of apoptotic from necrotic cells.
Other secondary labeling is possible, e.g., membrane surface staining with a phycoerythrin or TRITC-labeled monoclonal antibody for further cellular characterization.
Annexin-V-FLUOS detects apoptotic cells in suspension cells using flow cytometry (FACS) or fluorescence microscopy, by binding to phosphatidylserine on the outer leaflet of apoptotic cell membranes. A simultaneous labeling with, e.g., propidium iodide (PI) is needed for differentiation of apoptotic from necrotic cells.
Other secondary labeling is possible, e.g., membrane surface staining with a phycoerythrin or TRITC-labeled monoclonal antibody for further cellular characterization.
Preparation Note
Working concentration: Amount of rGFP recommended for:
Detection: Annexin-V-FLUOS can be directly detected in FACS analysis and immunochemistry without a secondary detection system.
Sample material: Cell lines and freshly isolated cells.
- SDS-PAGE (Coomassie stained): 1μg
- Western blot: 5ng
Detection: Annexin-V-FLUOS can be directly detected in FACS analysis and immunochemistry without a secondary detection system.
Sample material: Cell lines and freshly isolated cells.
Other Notes
For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
No data available
flash_point_c
No data available
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Paula Piccolo Maitan et al.
Frontiers in cell and developmental biology, 9, 772254-772254 (2021-12-07)
Classical in vitro fertilization (IVF) is still poorly successful in horses. This lack of success is thought to be due primarily to inadequate capacitation of stallion spermatozoa under in vitro conditions. In species in which IVF is successful, bicarbonate, calcium
Duncan C Humphries et al.
Frontiers in pharmacology, 13, 949264-949264 (2022-08-26)
Rationale: Galectin-3 (Gal-3) drives fibrosis during chronic lung injury, however, its role in acute lung injury (ALI) remains unknown. Effective pharmacological therapies available for ALI are limited; identifying novel concepts in treatment is essential. GB0139 is a Gal-3 inhibitor currently
Didac Carmona-Gutierrez et al.
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.), 10(22), 3973-3978 (2011-11-11)
The activation of ceramide-generating enzymes, the blockade of ceramide degradation, or the addition of ceramide analogues can trigger apoptosis or necrosis in human cancer cells. Moreover, endogenous ceramide plays a decisive role in the killing of neoplastic cells by conventional
Didac Carmona-Gutierrez et al.
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.), 12(11), 1704-1712 (2013-05-10)
Following microbial pathogen invasion, the human immune system of activated phagocytes generates and releases the potent oxidant hypochlorous acid (HOCl), which contributes to the killing of menacing microorganisms. Though tightly controlled, HOCl generation by the myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-chloride system of neutrophils/monocytes
H Rassoolzadeh et al.
Cell death & disease, 7, e2267-e2267 (2016-06-17)
Altered expression of the multifunctional protein WRAP53β (WD40 encoding RNA Antisense to p53), which targets repair factors to DNA double-strand breaks and factors involved in telomere elongation to Cajal bodies, is linked to carcinogenesis. While loss of WRAP53β function has
Articles
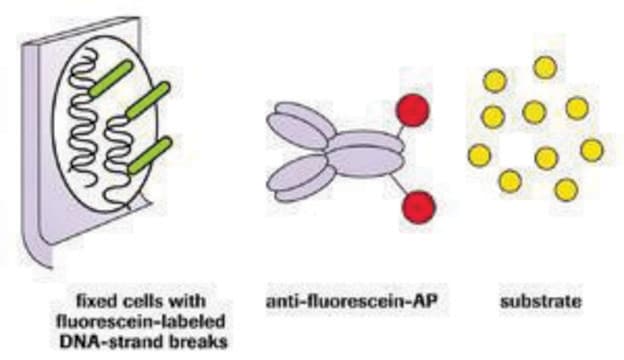
Cellular apoptosis assays to detect programmed cell death using Annexin V, Caspase and TUNEL DNA fragmentation assays.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service