A9210
Annexin V FITC Conjugate from human placenta
Synonym(s):
Annexin V, Calphosbindin I, Lipocortin V, PAP-1
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(1)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41106305
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
form
buffered aqueous solution
Quality Level
extent of labeling
1-2 mol FITC per mol annexin V
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
Gene Information
human ... ANXA5(308)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
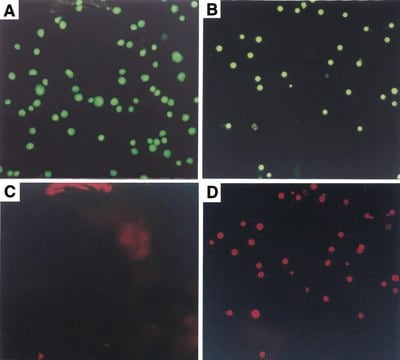
For detection of apoptotic cells by flow cytometry or fluorescence microscopy.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Annexins are ubiquitous homologous proteins that bind phospholipids in the presence of calcium.
Annexins are ubiquitous homologous proteins that bind phospholipids in the presence of calcium. The cellular changes involved in the apoptotic process include loss of phospholipid asymmetry during the early stages. This phenomenon is universal and is not limited to stimulus or to mammalian cells, but also occurs in insect and plant cells. In living cells, phosphatidylserine is transported to the inside of the lipid bilayer by the Mg2+ATP dependent enzyme, aminophospholipid translocase. At the onset of apoptosis, phosphatidylserine becomes translocated to the external surface of the cell membrane. Since the movement of phosphatidylserine from the internal membrane surface to the external surface is an early indicator of apoptosis, annexin V and its conjugates that interact strongly and specifically with phosphatidylserine may be used to detect apoptosis. Annexin V conjugates can be used to detect apoptotic cells significantly earlier than DNA-based assays. Fluorescent dye labeled annexin V have applications in flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy, and laser scanning cytometry.
Packaging
Package size based on protein content
Physical form
Solution in 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, containing 100 mM NaCl.
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Li-Min Zhu et al.
Frontiers in oncology, 11, 690878-690878 (2021-07-20)
Feiyanning formula (FYN) is a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) prescription used for more than 20 years in the treatment of lung cancer. FYN is composed of Astragalus membranaceus, Polygonatum sibiricum, Atractylodes macrocephala, Cornus officinalis, Paris polyphylla, and Polistes olivaceous, etc.
Melek Aydın et al.
European journal of breast health, 17(3), 274-282 (2021-07-16)
Liposomal cancer treatment strategies are useful in removing the side effects that were the main concern in recent years. In this study, we prepared microbubble (MBs) conjugated with DOX-loaded liposomes (DOX-loaded MBs) and investigated their effectiveness in in vitro breast
Carolina Orlando Vaso et al.
Pharmaceutics, 14(5) (2022-05-29)
Histoplasma capsulatum is a fungus that causes histoplasmosis. The increased evolution of microbial resistance and the adverse effects of current antifungals help new drugs to emerge. In this work, fifty-four nitrofurans and indoles were tested against the H. capsulatum EH-315
Caroline B Costa-Orlandi et al.
Pharmaceutics, 15(5) (2023-05-27)
The ability of dermatophytes to live in communities and resist antifungal drugs may explain treatment recurrence, especially in onychomycosis. Therefore, new molecules with reduced toxicity that target dermatophyte biofilms should be investigated. This study evaluated nonyl 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate (nonyl) susceptibility and
Amanda Weege S Martins et al.
Environmental science and pollution research international, 28(46), 65127-65139 (2021-07-07)
Roundup Transorb® (RDT) is a glyphosate-based herbicide commonly used in agricultural practices worldwide. This herbicide exerts negative effects on the aquatic ecosystem and affects bioenergetic and detoxification pathways, oxidative stress, and cell damage in marine organisms. These effects might also
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service