26745
Cholesterol Esterase from porcine pancreas
lyophilized, powder, white, ~35 U/mg
Synonym(s):
bile salt-dependent lipase, bile salt-stimulated lipase, carboxyl ester lipase, nonspecific lipase, pancreatic lysophospholipase, Cholesterol Esterase from hog pancreas, Sterol-ester acylhydrolase
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
Porcine pancreas
Quality Level
form
powder
quality
lyophilized
specific activity
~35 U/mg
mol wt
Mr ~440000
color
white
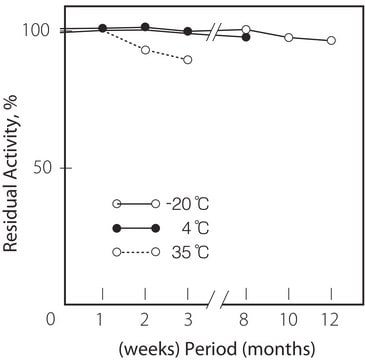
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
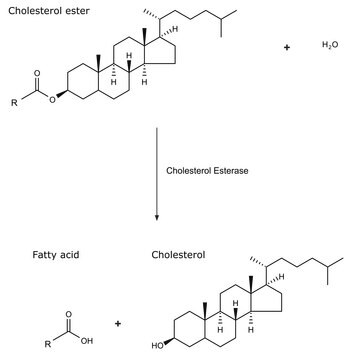
General description
Pancreatic cholesterol esterase (CEase), also known as bile salt stimulated lipase, is a serine hydrolase belonging to the α/β hydrolase family of enzymes. They are released from the exocrine pancreas. Serine 194, histidine 435 and aspartate 320 represent the catalytic triad of the enzyme.
Application
- in an in vitro simulated digestion model to improve the hydrolysis of carotenoid esters in the intestinal phase
- to analyze the bioavailability of phytosterol and cholesterol in the aqueous micellar phase of an in vitro simulated digestion model
- as a standard in enzyme activity assay
Biochem/physiol Actions
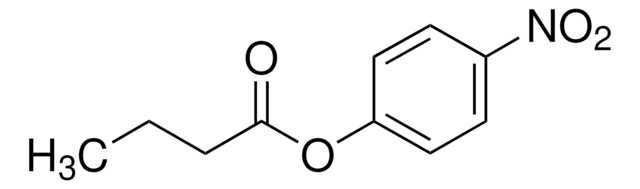
Unit Definition
Other Notes
signalword
Danger
hcodes
pcodes
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service