C2506
Cytochrome c from equine heart
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
Synonym(s):
Cytochrome c from horse heart
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
horse heart
assay
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
form
powder
mol wt
12,384
technique(s)
cell based assay: suitable
solubility
H2O: soluble 10 mg/mL
suitability
suitable for molecular biology
UniProt accession no.
application(s)
cell analysis
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
horse ... CYCS(100053958)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
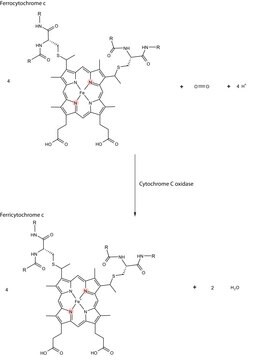
- in the reduction of ferricytochrome c by xanthine oxidase-generated superoxide radicals
- as an analyte by the single droplet deposition method using MALDI mass spectra
- as a terminal electron acceptor in the assay of standard cytochrome c reductase activity
- in cytochrome c oxidase histochemistry
- in the measurement of cytochrome C oxidase activity
- as a component of phosphate buffer for the detection and evaluation of complex IV activity using blue-native gel electrophoresis (BN-PAGE)
- for detection of extracellular superoxide anion (ECSA) in isolated kidney phagocytes
Biochem/physiol Actions
Preparation Note
Other Notes
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Chromatograms
application for HPLCapplication for HPLCapplication for HPLCOur team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service