추천 제품
생물학적 소스
microbial
Quality Level
제품 라인
BioReagent
분석
≥99% (GC)
양식
powder
기술
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
mp
88-92 °C (lit.)
solubility
water: 100 mg/mL, clear, colorless to faintly yellow
저장 온도
2-8°C
SMILES string
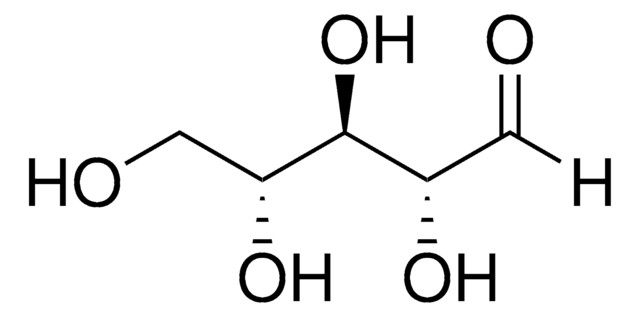
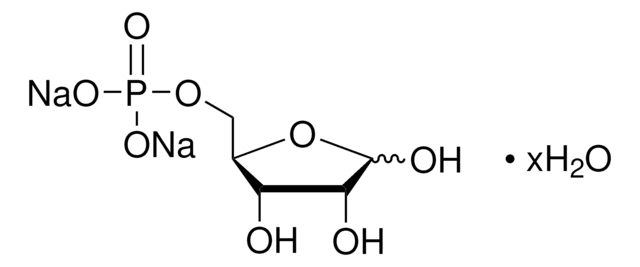
OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)C([H])=O
InChI
1S/C5H10O5/c6-1-3(8)5(10)4(9)2-7/h1,3-5,7-10H,2H2/t3-,4+,5-/m0/s1
InChI key
PYMYPHUHKUWMLA-LMVFSUKVSA-N
유사한 제품을 찾으십니까? 방문 제품 비교 안내
애플리케이션
D-(−)-Ribose has been used for microtissue fabrication and in cell culture.
생화학적/생리학적 작용
Ribose is an aldopentose monosaccharide that is phosphorylated into D-ribose 5-phosphate by ribokinase. Ribose-5-phosphate supports the biosynthesis of tryptophan and histidine and is a component of the pentose phosphate pathway.
적합성
This D-ribose has been qualified for use as a supplement in cell culture.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
가장 최신 버전 중 하나를 선택하세요:
시험 성적서(COA)
Lot/Batch Number
이미 열람한 고객
Matthew Walker et al.
Scientific reports, 10(1), 7696-7696 (2020-05-08)
When stretched, cells cultured on 2D substrates share a universal softening and fluidization response that arises from poorly understood remodeling of well-conserved cytoskeletal elements. It is known, however, that the structure and distribution of the cytoskeleton is profoundly influenced by
Development and characterization of a 3D multicell microtissue culture model of airway smooth muscle
West AR, et al.
American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 304(1), 4-16 (2012)
Matthew Walker et al.
APL bioengineering, 4(3), 036107-036107 (2020-09-29)
Characterizing the time-dependent mechanical properties of cells is not only necessary to determine how they deform but also to understand how external forces trigger biochemical-signaling cascades to govern their behavior. At present, mechanical properties are largely assessed by applying local
Hyperactive Rac1 drives MAPK-independent proliferation in melanoma by assembly of a mechanosensitive dendritic actin network
Mohan AS, et al.
bioRxiv (2018)
Pedro Vizán et al.
International journal of cancer, 124(12), 2789-2796 (2009-03-03)
Cell cycle regulation is dependent on multiple cellular and molecular events. Cell proliferation requires metabolic sources for the duplication of DNA and cell size. However, nucleotide reservoirs are not sufficient to support cell duplication and, therefore, biosynthetic pathways should be
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.