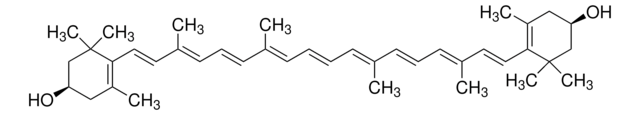
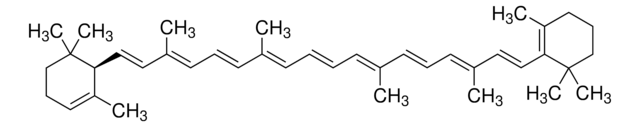
おすすめの製品
由来生物
synthetic
品質水準
アッセイ
≥96.0% (UV)
フォーム
powder
損失
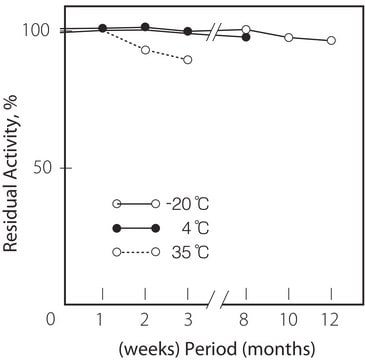
≤0.5% loss on drying, 20 °C (HV)
mp
137-141 °C
溶解性
chloroform: 1 mg/mL, clear to very faintly turbid, intense red-orange
保管温度
−20°C
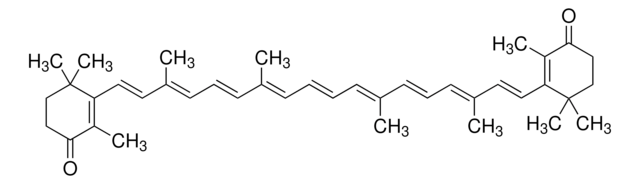
SMILES記法
[H]C(=O)\C(C)=C\C=C\C(C)=C\C=C\C=C(C)\C=C\C=C(C)\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C
InChI
1S/C30H40O/c1-24(13-8-9-14-25(2)16-11-18-27(4)23-31)15-10-17-26(3)20-21-29-28(5)19-12-22-30(29,6)7/h8-11,13-18,20-21,23H,12,19,22H2,1-7H3/b9-8+,15-10+,16-11+,21-20+,24-13+,25-14+,26-17+,27-18+
InChI Key
DFMMVLFMMAQXHZ-DOKBYWHISA-N
類似した製品をお探しですか? 訪問 製品比較ガイド
アプリケーション
- 複合天然抽出物の選択的分析クリーンアップの課題への取り組み:クロロフィル除去の興味深い事例:この研究では、複合天然抽出物の選択的分析クリーンアップの方法論を概説しています。この方法は、trans-β-アポ-8′-カロテナールの純度と安定性を向上させる目的で応用することができ、特にライフサイエンス分野の製造や研究開発の分野で有用です。このアプローチは、合成や保管中の生理活性化合物の完全性を維持するために極めて重要となります(Bijttebier et al., 2014)。
生物化学的/生理学的作用
その他情報
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
10810-BULK:
10810-1G:
10810-5G:
10810-VAR:
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)