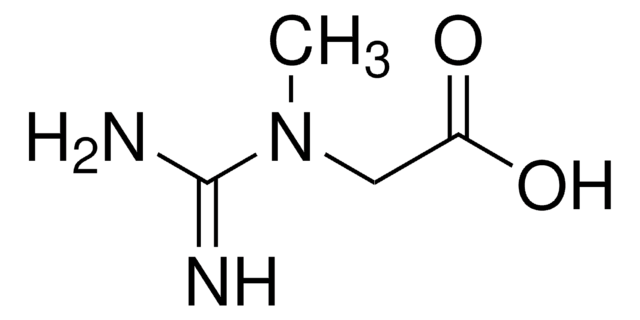
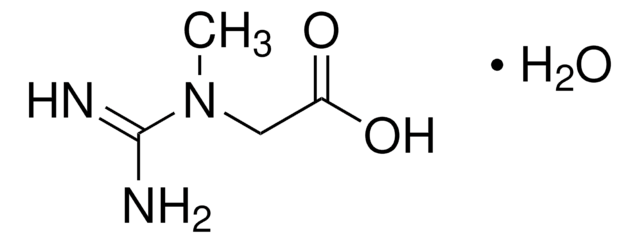
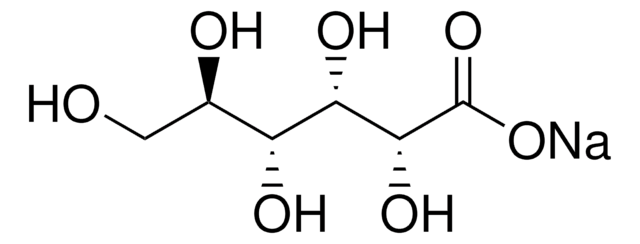
추천 제품
일반 설명
Aspartic acid (or aspartate) is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is naturally synthesized by mammals. Aspartate presents many biochemical roles:
In the L-conformation, aspartic acid is a building block in the production of proteins, as well as aiding in many bodily functions, including the urea cycle, gluconeogenesis, and Krebs Cycle, a process that generates adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Aspartic acid also works as a neurotransmitter. The D-Aspartate conformation is linked to neurogenesis and endocrine systems.
In the L-conformation, aspartic acid is a building block in the production of proteins, as well as aiding in many bodily functions, including the urea cycle, gluconeogenesis, and Krebs Cycle, a process that generates adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Aspartic acid also works as a neurotransmitter. The D-Aspartate conformation is linked to neurogenesis and endocrine systems.
애플리케이션
The Aspartate Metabolite Library is a kit that contains a selection of 23 metabolite involved in Aspartate metabolism.These may be used for general research, as reagents or as reference compounds in analytical procedures.
생화학적/생리학적 작용
Aspartate roles and metabolites:
- Aspartate is synthesized by transamination of oxaloacetate through the actions of Aspartate aminotransferase and pyridoxal 5′- phosphate. Aspartyl-tRNA synthase can then couple the aspartate to aspartyl tRNA for protein synthesis.
- Aspartate carries the reducing equivalents in the mitochondrial Malate-Aspartate shuttle, which uses the ready interconversion of aspartate and oxaloacetate.
- N-acetylaspartate synthase, present in the cytoplasm, converts aspartate to N-acetylaspartate, a brain metabolite that regulates dopamine.
- Asparagine is biosynthesized by Asparagine synthetase from aspartate, glutamine, and ATP. Asparagine is involved in the metabolic control of cell functions in nerve and brain tissue.
- Arginosuccinic acid is synthesized from aspartate, citrulline and ATP through the action of Argininosuccinate synthase, one of the enzymes of the urea cycle. In this metabolic pathway, neurotoxic ammonia, produced by protein catabolism, is converted into urea in the liver.
- Fumaric acid is synthesized from Argininosuccinic acid via an Argininosuccinate lyase, which is an enzyme in the Citric Acid Cycle.
- Inosinic acid, aspartic acid and GTP are interconverted to GDP and AMP by the Adenylosuccinate synthetase isozyme 1. This process is involved in the purine nucleotide cycle which regulates nucleotides levels in various tissues.
- Aspartate transcarbamoylase catalyzes the synthesis of N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate from carbamoyl phosphate and aspartate that are involved in the de novo biosynthesis of pyrimidines.
- Beta alanine is formed by decarboxylation of aspartate by Glutamate decarboxylase 1 in the cytoplasm.
- L-aspartate is converted to D-aspartate through the action of a D-aspartate racemase. D-aspartate contributes to the synthesis and release of glucocorticoids, prolactin, oxytocin, and steroids. D-aspartate plays an important role in the brain activity of mammals.
성분
Contains 10 mg each of Aspartate metabolism metabolite standards packaged individually.
키트 구성품 역시 별도로 이용 가능함
제품 번호
설명
SDS
- A2252Adenosine 5′-monophosphate monohydrate, from yeast, ≥97%SDS
- A2383Adenosine 5′-triphosphate disodium salt hydrate, Grade I, ≥99%, from microbialSDS
- A5707Argininosuccinic acid disodium salt hydrate, ≥80%SDS
- 146064β-Alanine, 99%SDS
- C4135Carbamyl phosphate disodium salt, ≥80%SDS
- C7629L-Citrulline, ≥98% (TLC)SDS
- 219096D-Aspartic acid, ReagentPlus®, 99%SDS
- F6625Flavin adenine dinucleotide disodium salt hydrate, ≥95% (HPLC), powderSDS
- 47910Fumaric acid, ≥99.0% (T)SDS
- G7252Guanosine 5′-diphosphate tris salt from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Type VI, ≥92.5%SDS
- G9002Guanosine 5′-triphosphate tris salt, ≥93% (HPLC), powderSDS
- I2879Inosine 5′-monophosphate from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, ≥98%SDS
- A5006L-Arginine, reagent grade, ≥98%SDS
- A0884L-Asparagine, ≥98% (HPLC)SDS
- 11189L-Aspartic acid, BioUltra, ≥99.5% (T)SDS
- G1251L-Glutamic acid, ReagentPlus®, ≥99% (HPLC)SDS
- G3126L-GlutamineSDS
- 00920N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid, ≥99.0% (T)SDS
- O4126Oxaloacetic acid, ≥97% (HPLC)SDS
- K1750α-Ketoglutaric acid, ≥98.5% (NaOH, titration)SDS
- P9255Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate hydrate, ≥98%SDS
- P8010Sodium pyrophosphate tetrabasic, ≥95%SDS
- 69037Ureidosuccinic acid, 98.0-102.0% (T)SDS
모두 보기 (23)
신호어
Danger
유해 및 위험 성명서
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
Lennarz W J, et al.
Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry, 600-605 (2004)
Kıvanç Birsoy et al.
Cell, 162(3), 540-551 (2015-08-02)
The mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC) enables many metabolic processes, but why its inhibition suppresses cell proliferation is unclear. It is also not well understood why pyruvate supplementation allows cells lacking ETC function to proliferate. We used a CRISPR-based genetic
Ifeanyi J Arinze
Biochemistry and molecular biology education : a bimonthly publication of the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 33(3), 165-168 (2005-05-01)
Some metabolic processes are readily understood because they are circumscribed in metabolic pathways that have clearly identifiable beginning points, end products, and other features. Other metabolic pathways that do not appear to be straightforward pose difficulties for students. One such
F Errico et al.
Translational psychiatry, 4, e417-e417 (2014-07-30)
D-aspartate (D-Asp) is an atypical amino acid, which is especially abundant in the developing mammalian brain, and can bind to and activate N-methyl-D-Aspartate receptors (NMDARs). In line with its pharmacological features, we find that mice chronically treated with D-Asp show
Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids and Amino Acid Degradation.
Litwack G, et al.
Human Biochemistry and Disease, 63-94 (2018)
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.