341631
Bovine Fibronectin
from bovine plasma, liquid, suitable for cell culture
Synonym(s):
Fibronectin, Bovine Plasma
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Fibronectin, Bovine Plasma,
description
Merck USA index - 14, 4075
Quality Level
form
liquid
manufacturer/tradename
Calbiochem®
storage condition
OK to freeze
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
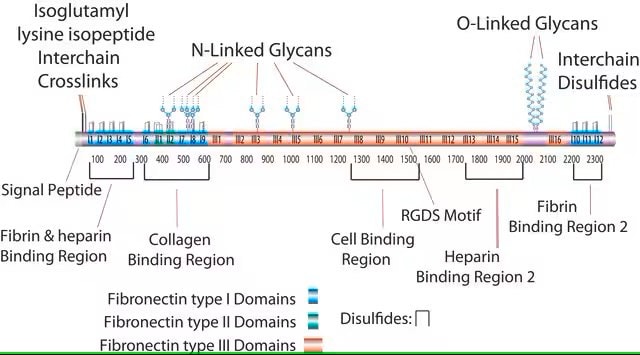
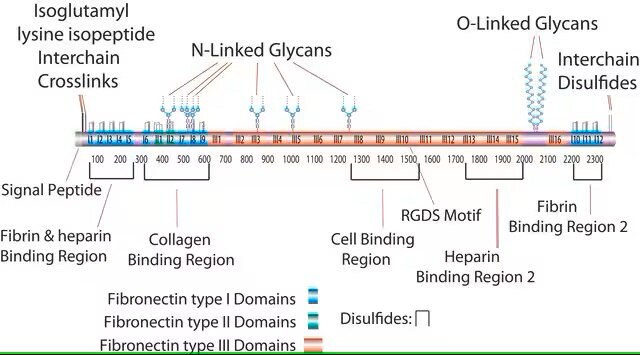
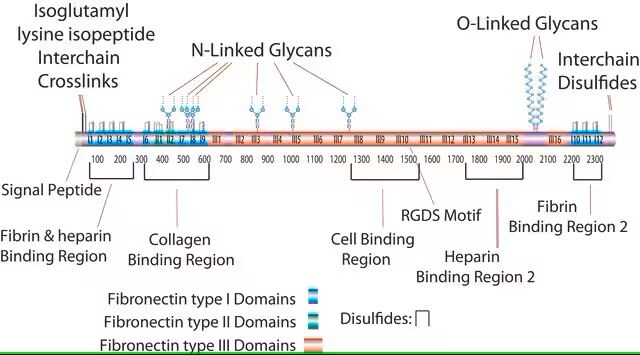
Fibronectin is an extracellular matrix (ECM) glycoprotein. It is expressed in various cell types. Fibronectin exists as a dimer and is made up of identical subunits which are linked covalently via a disulfide bond at their C-termini.
Application
Fibronectin, Bovine Plasma has been used as an extracellular matrix (ECM) substrate to coat dishes or polyacrylamide hydrogels for adhering:
- human melanoma cancer cells
- human breast epithelial cells
- mouse embryonic fibroblasts
Biochem/physiol Actions
Fibronectin plays a role in cell adhesion, growth, migration, and differentiation. It binds to several molecules such as integrins, heparin, fibrin, and collagen.
Packaging
Please refer to vial label for lot-specific concentration.
Warning
Toxicity: Standard Handling (A)
Physical form
In 150 mM NaCl, 20 mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.3.
Reconstitution
Following initial thaw, aliquot and freeze (-20°C).
Analysis Note
single band by SDS-PAGE
Legal Information
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Purva Singh et al.
Annual review of cell and developmental biology, 26, 397-419 (2010-08-10)
In the process of matrix assembly, multivalent extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins are induced to self-associate and to interact with other ECM proteins to form fibrillar networks. Matrix assembly is usually initiated by ECM glycoproteins binding to cell surface receptors, such
Jordi Pijuan et al.
Frontiers in cell and developmental biology, 7, 107-107 (2019-07-02)
Cell migration is a key procedure involved in many biological processes including embryological development, tissue formation, immune defense or inflammation, and cancer progression. How physical, chemical, and molecular aspects can affect cell motility is a challenge to understand migratory cells
Guillaume Jacquemet et al.
The Journal of cell biology, 216(10), 3387-3403 (2017-08-03)
Defective filopodia formation is linked to pathologies such as cancer, wherein actively protruding filopodia, at the invasive front, accompany cancer cell dissemination. Despite wide biological significance, delineating filopodia function in complex systems remains challenging and is particularly hindered by lack
Fibronectin at a glance.
Roumen Pankov et al.
Journal of cell science, 115(Pt 20), 3861-3863 (2002-09-24)
Joseph A Brazzo et al.
Journal of cell science, 134(12) (2021-06-22)
Cell cycle control is a key aspect of numerous physiological and pathological processes. The contribution of biophysical cues, such as stiffness or elasticity of the underlying extracellular matrix (ECM), is critically important in regulating cell cycle progression and proliferation. Indeed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service