10165875001
Roche
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6P-DH)
from Leuconostoc mesenteroides
Synonym(s):
G6P-DH, Glucose-6-Phosephate Dehydrogenase
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
bacterial (Leuconostoc mesenteroides)
Quality Level
form
solution
suspension
specific activity
~550 units/mg protein (At 25 °C (650 U/mg at 30 °C) with glucose-6-P and NAD as the substrates.)
mol wt
dimer 110 kDa
packaging
pkg of 1 mL (1,000 U)
manufacturer/tradename
Roche
concentration
≥0.1-1.0 % (w/w)
technique(s)
activity assay: suitable
color
white
optimum pH
7.0-8.5(maximal activity at 7.8)
solubility
water: miscible
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
application(s)
life science and biopharma
foreign activity
6-PGDH <0.001%
CK <0.001%
GR <0.01%
HK <0.05%
NADH oxidase <0.02%
PGI <0.01%
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
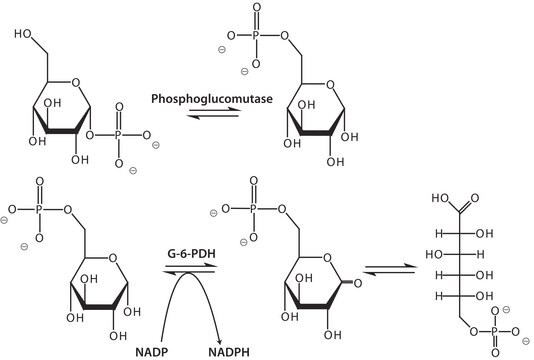
General description
Specificity
LG6P-DH does not react with fructose-6-phosphate, fructose-1,6-biphosphate, glucose-1-phosphate or ribose-1-phosphate. LG6P-DG will oxidize 2-deoxy-glucose-6-phosphate with NADP, but not with NAD as coenzyme. There is a slow reaction with D-glucose.
Heat inactivation: The ammonium sulfate suspension is not inactivated when heated to temperatures ≤ 50 °C for 10 minutes. At temperatures > 60 °C the enzyme is rapidly inactivated.
Application
Quality
Unit Definition
Unit Definition: One unit (U) LG6P-DH oxidizes 1 mol of glucose-6-phosphate and reduces 1 mol of NAD in 1 minute at +25 °C and pH 7.8.
Physical form
Preparation Note
Analysis Note
Other Notes
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
does not flash
flash_point_c
does not flash
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service