おすすめの製品
アプリケーション
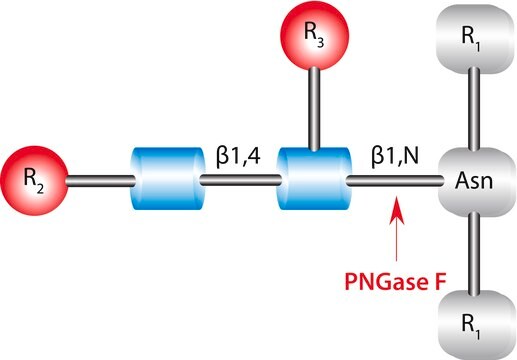
ノイラミニダーゼは、α(2→6)、α(2→3)、α(2→8)、α(2→9)結合(親和性の順に示す)の加水分解により、非還元型非分枝型N-アセチルノイラミン酸およびN-グリコリルノイラミン酸をすべて切断する性能をもつ重要な脱グリコシル酵素です。高濃度の本酵素と長時間インキュベーションを使用することにより、分枝型シアル酸も切断できます。脱シアル化糖タンパク質は、多様なエキソグリコシダーゼで処理することによりさらに特徴づけられ、部分的または完全なO-脱グリコシル化が生じます。精製、構造解析、塩基配列決定には一般に、SDS-PAGEおよびMALDI-TOF MSが用いられます。これらのテクノロジーにより、不均一性が解消され、糖タンパク質由来の電荷も除去されます。
包装
5×濃度の反応バッファ-が付属します。
品質
特別な組成のバッファ-溶液ですので、最良の酵素安定性とアッセイ感度が得られます。
単位の定義
1unitは、pH 5.5, 37℃で、1分間あたり、2-(4-メチルウンベリフェリル)α-D-N-アセチルノイラミン酸から1nmolの4-メチルウンベリフェロンを遊離させる酵素量です。
物理的形状
凍結乾燥粉末
関連製品
製品番号
詳細
価格
シグナルワード
Danger
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Resp. Sens. 1
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
N3786-VAR:
N3786-1SET:
N3786-1PKG:
N3786-BULK:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
Hongyun Li et al.
PloS one, 11(2), e0148238-e0148238 (2016-02-02)
Recent studies have shown that cerebral apoD levels increase with age and in Alzheimer's disease (AD). In addition, loss of cerebral apoD in the mouse increases sensitivity to lipid peroxidation and accelerates AD pathology. Very little data are available, however
Natallia Makarava et al.
Acta neuropathologica communications, 6(1), 92-92 (2018-09-14)
Last decade witnessed an enormous progress in generating authentic infectious prions or PrPSc in vitro using recombinant prion protein (rPrP). Previous work established that rPrP that lacks posttranslational modification is able to support replication of highly infectious PrPSc with assistance
Johan Nordholm et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 288(15), 10652-10660 (2013-03-01)
Interactions that facilitate transmembrane domain (TMD) dimerization have been identified mainly using synthetic TMDs. Here, we investigated how inherent properties within natural TMDs modulate their interaction strength by exploiting the sequence variation in the nine neuraminidase subtypes (N1-N9) and the
Audu J Natala et al.
Journal of medical entomology, 50(1), 85-93 (2013-02-23)
Amblyomma variegatum F. are obligate hematophagous ectoparasites of livestock that serve as the vectors of Ehrlichia ruminantium (formerly known as Cowdria ruminantium), the causative agent of heartwater disease. In the light of the fact that they are blood-feeding, their salivary
Dominic Meusch et al.
Nature, 508(7494), 61-65 (2014-02-28)
Tripartite Tc toxin complexes of bacterial pathogens perforate the host membrane and translocate toxic enzymes into the host cell, including in humans. The underlying mechanism is complex but poorly understood. Here we report the first, to our knowledge, high-resolution structures
資料
Glycan Sequencing Using Exoglycosidases
Learn about O-linked glycan strategies, O-glycosidase actions, how to remove sialic acid residues, β-Elimination, and O-glycan modifications.
Understand sialic acid structure, function, signaling, and modifications. Easily find products for sialic acid research.
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)